Data Structure and Algorithms
Data Structure
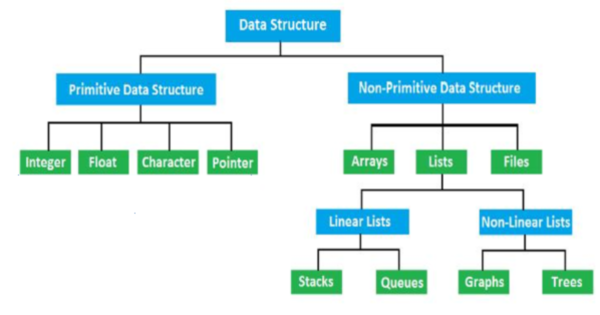
@EduPlusOne, we start with the basic understanding the concept of complexity and introduction to programming. Every piece of code you write you should be able to derive both time and space complexity. Then we move to the operations insert, delete, search, traversal on data structures such as Arrays, Linked List, Strings, Stacks, Queues, Sorting, Searching, Prime numbers, String Manipulations, Matrix Manipulation, Fibonacci Numbers, Palindrome and then more linear data Structures such as Binary Tree, Binary Tree search. Highlights of the topics are given below.
Memory and variables – locations, addresses, definitions and declarations; program structure, data types, operators, and expressions, expression evaluation: operator, precedence and associativity, expression evaluation with different data types: type conversion (implicit and explicit), relational, equality, and logical operators
Control Structures
Control statements- sequential, conditional and iterative, if-statement (if-else ladder, nested if, compound if), switch statement (multiway selection), for statement (nested for), while and do-while loops. Sample programs illustrating the use of control statements as basic building blocks.
Data Structure - Arrays
One dimensional and multi-dimensional random access lists: declaring, initializing, and accessing list elements, searching algorithms: linear and binary, sorting algorithms: selection, insertion and bubble sort, implementing stacks and queues using arrays.
Data Structure - Functions and Pointers
Need of functions: modularity and reuse, declaration and definition, scope of data and problem solving, Recursion-self recursive structures, Merge sort, Binary Search using recursion.<br /> Introduction to pointers, argument passing to functions: by value and by reference and pointer arithmetic
Data Structure - Strings
Character arrays as strings, standard library string functions: syntax and implementation, string manipulation with and without header file string.
Data Structure - Heterogeneous Data Types
Memory layout – implicit vs. explicit allocation; static vs. dynamic allocation; new and delete for dynamic allocation/deallocation, user defined types: typedef, # define, structures, pointer to structure, union, enumerated data types, self referential structures
Dynamic Data Structures
Linked Lists: inserting, searching and deleting nodes, implementing stacks and queues using linked lists, merging of linked lists, Doubly linked lists, Binary trees and BST, AVL Trees, Graphs (representation using adjacency list and matrix), BFS and DFS Algorithms with coding, Shortest route algorithm, Hash Tables and Map
Course Duration
10 Weeks
Course Fees for group classes
INR 15000
